In an era where the internet plays an integral role in our daily lives, making your website accessible to all online shoppers is not just a good practice; it’s a necessity. With the holiday season approaching, it’s the perfect time to ensure that your website accommodates everyone, including those with disabilities. Web accessibility isn’t just about complying with regulations; it’s about creating an inclusive online space that welcomes every potential customer. This article will guide you through the essential steps to make your website accessible to all online shoppers, not only for the holidays but for the long term.
Understanding Web Accessibilty
Web accessibility refers to designing websites and online content in a way that ensures everyone, regardless of their abilities or disabilities, can perceive, navigate, and interact with the web effectively. Disabilities that affect web users include visual, auditory, cognitive, motor, and speech impairments. When your website is accessible, it’s more user-friendly and can cater to a broader audience, which can ultimately boost your sales and reputation.
Why Web Accessibility Matters for Online Shoppers
Legal Compliance
Many countries have implemented laws that require websites to be accessible to people with disabilities. By ensuring your website is accessible, you not only avoid potential legal issues but also demonstrate your commitment to inclusivity and social responsibility.
Expanded Audience
Approximately 15% of the world’s population lives with some form of disability. By making your website accessible, you open your doors to this sizable demographic, potentially expanding your customer base significantly.
Improved User Experience
An accessible website benefits everyone, not just those with disabilities. It provides a better user experience for all visitors, leading to increased engagement and conversion rates.
Boost Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
Accessibility features, such as alt text for images and well-structured content, can improve your website’s search engine optimization (SEO). This means more visibility and potential traffic from search engines.
Now, let’s get into the practical steps you can take to make your website accessible to all online shoppers.
Making Your Website Accessible
1. Conduct an Accessiblity Audit
Before making any changes, it’s essential to assess your website’s current accessibility level. This can be done through automated tools, manual testing, or by hiring an accessibility consultant. These audits will help you identify areas that need improvement and create a roadmap for the changes you need to make.
Assessing Your Website
A website assessment involves an analysis of your website’s design, functionality, and feedback. It helps you identify areas where visitors might be experiencing difficulties.
2. Prioritize Accessibility Features
Once you have a clear picture of your website’s accessibility status, prioritize the most critical features to address. Some common accessibility features to consider include:
Alt Text for Images
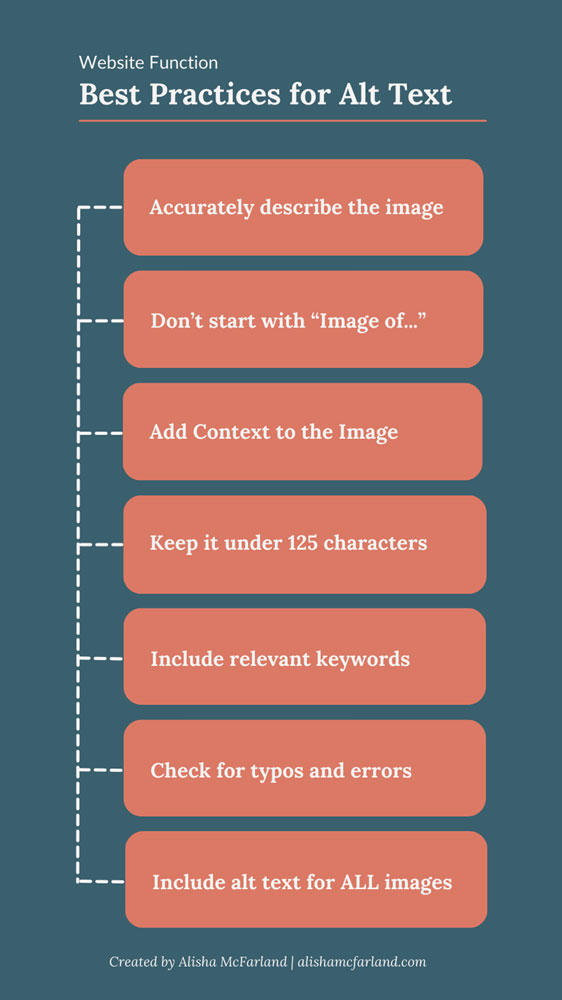
Providing descriptive alt text for images allows screen readers to convey the content to visually impaired users and is one of the most basic yet crucial accessibility practices. Alt text should convey the content and purpose of the image, helping visually impaired users understand its context. Avoid using generic descriptions like “image123.jpg” and be specific and concise.
Keyboard Navigation
Ensure that all interactive elements and content are navigable and usable via a keyboard, as some users may not be able to use a mouse or anyone with motor impairments. Test your website’s functionality using only a keyboard to ensure all interactive elements, buttons, and links are accessible and can be activated without a mouse.
Headings and Structure
Properly structured content with headings makes it easier for screen readers to interpret and for users to skim through your content. Semantic HTML tags, such as headings (h1, h2, h3, etc.), lists, and tables, provide structure to your content. Properly structuring your content not only aids in accessibility but also improves SEO. Use headings to outline the hierarchy of your content, making it easier for screen readers to interpret.
Color Contrast
Maintain a sufficient color contrast between text and background to aid users with low vision or color blindness. Maintain a sufficient color contrast ratio between text and background colors. This ensures that text is readable for users with low vision or color blindness. Several online tools can help you check and adjust color contrast.
Video Subtitles and Transcripts
Provide captions or transcripts for videos to assist users with hearing impairments. Videos and multimedia content are popular on websites, but they can pose challenges for users with disabilities. Provide closed captions for videos, audio descriptions for visual content, and transcripts for all multimedia elements. Additionally, offer a way for users to pause or control autoplaying videos.
Forms and Error Handling
Ensuring that online forms are designed with accessibility in mind is crucial for providing an inclusive experience to all users. This means providing clear and concise labels for form fields, offering instructions or hints for completing the form, and ensuring that users can navigate and submit forms using keyboard controls alone.
Error handling is equally essential, as it ensures that users, including those with disabilities, receive clear and informative error messages when they make mistakes while filling out forms. These messages should specify the error, suggest corrections, and be presented in a way that can be easily understood by screen readers and other assistive technologies.
By addressing forms and error handling accessibility, websites can guarantee that all users, regardless of their abilities, can effectively engage with their content and services.
Consistent Navigation
Consistent navigation ensures that users, including those with disabilities, can easily and predictably move around a website. Consistency in layout, menus, and navigation elements means that users can quickly learn how to find information, reducing confusion and frustration. Screen reader users, for example, rely on consistent navigation structures to efficiently explore and interact with web content. Accessibility is enhanced when headings and landmarks are consistently used to structure pages, and menus are labeled in a clear and logical manner. By prioritizing consistent navigation, websites become more user-friendly and accommodating, creating a more inclusive online environment for all visitors, regardless of their abilities or disabilities.
3. Test with Real Users
After implementing accessibility features, it’s crucial to conduct usability testing with real users, including individuals with disabilities. Their feedback will help you identify any remaining issues and fine-tune your website for a better user experience.
To do this, you can recruit individuals who have a range of disabilities that might affect their web browsing experience, such as visual, auditory, motor, or cognitive impairments. These testers can provide invaluable feedback by using various assistive technologies like screen readers, voice recognition software, or alternative input devices.
During the testing process, observe how users interact with your website, paying attention to any barriers they encounter or areas where they struggle. Encourage testers to share their experiences, suggestions, and concerns openly. This firsthand feedback helps uncover accessibility issues that might be challenging to identify through automated testing alone.
By involving real users with disabilities in your testing process, you can make informed improvements to your website and ensure that it genuinely meets the needs of a diverse audience.
Bonus Tip!
Web accessibility standards and technologies evolve. It’s essential to stay informed about the latest developments and guidelines, such as the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG). Regularly update your website to incorporate new accessibility features and ensure ongoing compliance.
Take Away
Inclusivity is not just a buzzword; it’s a fundamental principle that every online business should embrace. Making your website accessible to all online shoppers is not only a legal requirement in many regions but also a moral imperative. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can create an inclusive online space that welcomes all customers, not only for the holiday season but for years to come. Remember that web accessibility is an ongoing commitment, and continuous efforts to improve and maintain accessibility will benefit both your users and your business.


